Early Signs of Melanoma You Shouldn’t Ignore: Dermatologists Explain
Skin is the body’s largest organ — and often, the most overlooked when it comes to early signs of cancer. Among the different types of skin cancer, melanoma is the most aggressive and potentially deadly. But the good news? When caught early, melanoma skin cancer is highly treatable.
What Is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the melanocytes — the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives our skin its color. Unlike other skin cancers, melanoma can grow quickly and spread to other organs if not caught in time.
Though it accounts for only a small percentage of skin cancer cases, melanoma causes the majority of skin cancer-related deaths. So, understanding the early signs of melanoma can make a life-saving difference.
Is Melanoma Deadly?
Yes, melanoma can be deadly if left untreated or diagnosed in later stages. However, when detected early — especially in Stage 0 or Stage I — the survival rate is extremely high. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for localized melanoma is around 99%.
This makes awareness, prevention, and early detection essential tools in fighting this disease.
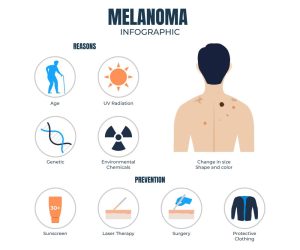
Melanoma Causes: What Increases Your Risk?
Dermatologists explain that melanoma causes can be both environmental and genetic. Here are the key factors:
- Excessive UV exposure from sunlight or tanning beds
- Fair skin, light eyes, and red or blonde hair
- Family history of melanoma or other skin cancers
- Having many moles or atypical (dysplastic) moles
- Weakened immune system due to other illnesses or treatments
- Older age, although melanoma is increasingly seen in younger adults
- Living near the equator or at higher altitudes, where UV exposure is stronger
Despite these risk factors, anyone — regardless of skin tone or age — can develop melanoma skin cancer.
Melanoma Symptoms: What Should You Look For?
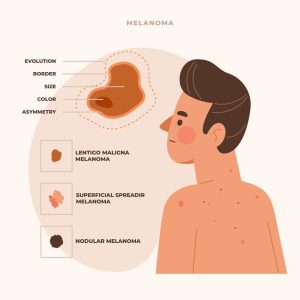
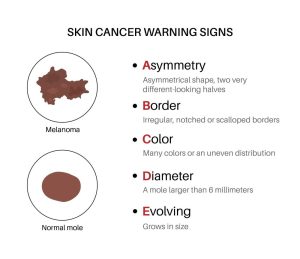
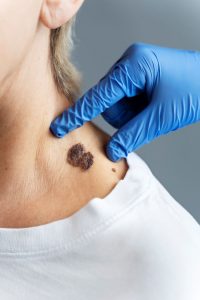
Melanoma often begins as a new spot on the skin or a change in an existing mole. Dermatologists recommend using the ABCDE rule to identify melanoma symptoms:
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B – Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined borders.
- C – Color: Multiple shades of brown, black, red, white, or blue.
- D – Diameter: Larger than 6 mm (about the size of a pencil eraser), though melanomas can be smaller.
- E – Evolving: Changes in size, shape, color, or new symptoms like itching or bleeding.
One of the most concerning signs is a new or changing mole, especially if it behaves differently from others on your body (called the “ugly duckling” sign). Melanoma spots can appear anywhere — including areas not typically exposed to the sun.
Melanoma on Face: A Special Warning
One of the most visible — and dangerous — forms of melanoma appears on the face. Melanoma on the face is often mistaken for age spots or harmless freckles. But any irregular spot on the face, especially one that changes quickly, bleeds, or crusts, should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Facial melanoma can affect the nose, cheeks, lips, ears, or eyelids, and due to the face’s sun exposure, it’s a common site for melanoma to develop.
Unusual Locations for Melanoma
While most people associate melanoma with sun-exposed areas, it can also develop in unexpected places, such as:
- Under the nails (subungual melanoma)
- Soles of the feet or palms of the hands
- Genital or anal regions
- Inside the mouth or eyes
These less visible forms can go unnoticed until advanced stages. That’s why regular full-body skin exams are essential.
Melanoma Stages: Understanding the Progression
Melanoma stages help determine the severity and spread of the disease. Here’s a basic breakdown:
- Stage 0 (In situ): Abnormal cells are present but haven’t spread beyond the outer skin layer.
- Stage I: Small tumours with no spread. Very high cure rate with surgery.
- Stage II: Larger tumours, possibly with high-risk features, but still localized.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Melanoma has spread to distant organs (lungs, liver, brain, etc.).
Early detection is key, as treatment options and success rates decrease significantly with advanced stages.

Diagnosis: How Is Melanoma Confirmed?
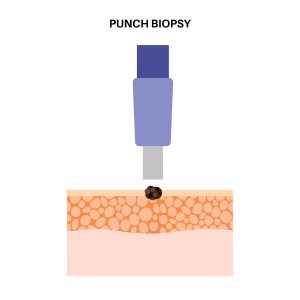
If your dermatologist suspects melanoma, the first step is usually a skin biopsy, where a small sample of the suspicious mole or lesion is removed and examined under a microscope.
Punch node biopsy –
A punch biopsy uses a cylindrical, sharp tool (like a mini cookie cutter) to remove a core of skin that includes all layers — epidermis, dermis, and superficial fat. It’s typically performed by dermatologists to diagnose skin conditions, including:
-
Skin cancers (like melanoma, basal cell carcinoma)
-
Rashes of unknown cause
-
Chronic skin conditions (like psoriasis, lupus)
Other tests may include:
- Lymph node biopsy (sentinel node biopsy)
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests like CT scans or PET scans for advanced cases
Once the melanoma is confirmed, your doctor will determine the stage and create a personalized melanoma treatment plan.
Melanoma Treatment Options
The choice of melanoma treatment depends on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as your overall health. Common treatments include:
1. Surgical Removal
- Often the first and only treatment for early-stage melanoma.
- Wide local excision is done to remove the tumour and surrounding tissue.
2. Immunotherapy
- Uses your immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Drugs like nivolumab or pembrolizumab help shrink tumours and improve survival.
3. Targeted Therapy
- For melanomas with specific genetic mutations (e.g., BRAF mutation).
- Drugs target and block the growth of cancer cells.
4. Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy is less commonly used, but may be recommended in some advanced cases.
5. Radiation Therapy
- Radiation helps control melanoma that has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Dermatologists stress that early detection reduces the need for aggressive treatment, making routine skin checks incredibly important.

Melanoma Spots vs. Benign Moles: When to Worry
Not all dark spots or moles are dangerous. However, it’s crucial to monitor them for any changes in size, shape, or colour.
Warning signs that a spot may be melanoma:
- Rapidly changing appearance
- Irregular edges or multiple colours
- Itching, bleeding, or crusting
- Pain or discomfort
If in doubt, get it checked. A simple examination can potentially save your life.
Prevention: Can You Avoid Melanoma?
While you can’t change your genetics or skin type, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Apply sunscreen (SPF 30+) daily, even on cloudy days
- Avoid tanning beds
- Wear protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats
- Seek shade during peak sunlight hours (10 AM – 4 PM)
- Perform monthly skin self-exams
- Visit a dermatologist annually for a full-body skin check
Final Thoughts
Melanoma is serious — but also highly treatable when caught early. By knowing the melanoma symptoms, paying attention to unusual melanoma spots, and being aware of changes, you can take control of your skin health.
Whether it’s a mole on your back, a freckle on your face, or a dark line under your nail — don’t ignore it. Melanoma on the face or elsewhere may be the first sign your body gives. Listen to it.
Dermatologists agree: early detection saves lives.
So, the next time you notice something new or changing on your skin, don’t wait. Schedule a visit with your dermatologist — because in the case of melanoma skin cancer, sooner is always better.